In today’s information-rich world, the ability to read and comprehend effectively is more critical than ever. Whether you are a student striving to excel in your studies, a professional aiming to stay current in your field, or simply an avid reader seeking to enjoy literature more deeply, strong reading comprehension skills are essential. This comprehensive guide explores some of the best strategies to enhance your understanding and retention of what you read. Here’s a free guide to download 😊😊😊😊😊
You may also like: Comprehension Worksheets
You may also like: Æsop’s Fables: A Version for Young Readers by J. H. Stickney and Aesop

1. Previewing the Text
Before delving into any text, it’s beneficial to preview it. This involves skimming through the headings, subheadings, and any highlighted or bolded terms. Look at images, charts, or graphs if they are present. This initial scan provides a roadmap of what to expect and primes your brain to receive and organize new information.
Want to teach Kids coding? Here’s something you might like: Kids Coding: Unlock the World of Programming Member area and video courses
Why it works: Previewing activates your prior knowledge and sets a purpose for reading. It makes it easier to absorb and retain information because you have an idea of what to look for and expect.
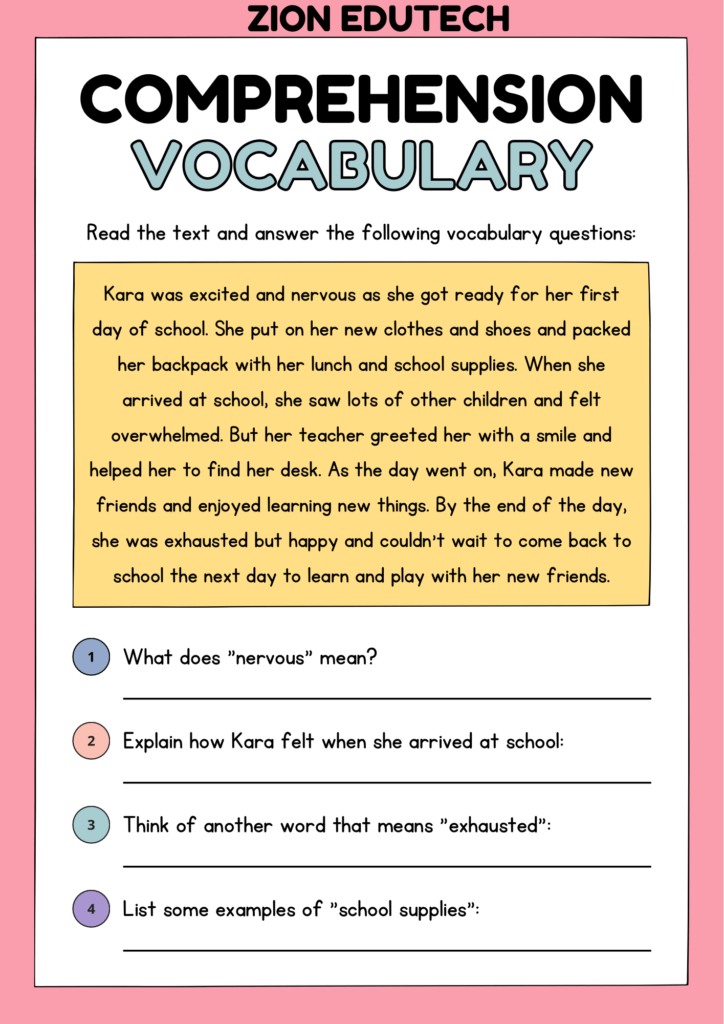
Comprehension Vocabulary Worksheet
2. Setting a Purpose
Having a clear purpose for reading can significantly enhance comprehension. Whether your goal is to learn something new, prepare for an exam, or enjoy a novel, knowing why you are reading helps you stay focused and engaged.
How to set a purpose: Before you start, ask yourself what you want to achieve. Are you looking for specific information? Do you want to understand the main arguments? Are you reading for pleasure or to gain a deeper understanding of a topic? Your purpose will guide your approach and help you extract relevant information.
3. Asking Questions
Engage actively with the text by asking questions. Before reading, jot down what you hope to learn. While reading, ask yourself why events are happening, what motivations characters might have, or what a particular concept means. After reading, ponder any remaining questions or areas of confusion.

Ask Questions like Who is Tom? Where did Tom go? What did Tom Found? What did Dog do?
Why it works: Asking questions keeps your mind engaged and curious. It transforms reading from a passive activity into an active quest for understanding. It also helps you focus on important details and connect different parts of the text.
4. Visualizing
Creating mental images of what you’re reading can significantly enhance comprehension. Picture the scenes, characters, or concepts described in the text. If you are reading about a historical event, imagine yourself there. For scientific concepts, visualize the processes.
Why it works: Visualizing helps solidify information in your memory by creating a vivid mental picture. It makes abstract or complex information more tangible and easier to recall.
You may also like: You’ll love these Flashcards!
5. Summarizing
After reading a section or chapter, pause and summarize the main points in your own words. This can be done verbally, in writing, or even through drawing.
Why it works: Summarizing forces you to distill the information to its essence. It reinforces your understanding and highlights any areas where your grasp may still be weak. It also helps with memory retention, as restating information in your own words strengthens neural connections.
6. Making Connections
Relate the text to your own experiences, other texts, or broader world knowledge. Making connections to something familiar helps anchor new information in your brain.
Types of connections:
- Text-to-self: How does this relate to my own life?
- Text-to-text: How does this compare to other things I’ve read?
- Text-to-world: How does this relate to the larger world or current events?
Why it works: Connecting new information to existing knowledge creates a network of related ideas. This enhances comprehension and retention by embedding new information into a familiar context.
7. Reflecting
After you have finished reading, take some time to reflect on the material. Think about the themes, the characters’ journeys, or the main arguments and conclusions. Consider how the text relates to your own life or to the world around you.
Why it works: Reflection deepens your understanding and helps you internalize the information. It turns passive reading into a more contemplative and meaningful experience. This process also encourages critical thinking and helps you develop your own perspectives.

Think about the Summer Season, picture it. Check the characters in passage.
8. Annotating
Don’t be afraid to write in the margins of your books, underline key phrases, or use sticky notes. Annotating can include summarizing points, noting questions, or marking important passages.
Why it works: This interactive approach keeps you engaged and allows you to capture your thoughts and reactions in real-time. It can be invaluable when reviewing the material later. Annotating also helps with retention and comprehension by actively involving you in the reading process.

9. Using Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers such as mind maps, Venn diagrams, and charts can help organize information visually. They are particularly useful for complex texts with multiple themes or for comparing and contrasting information.
Why it works: Graphic organizers provide a clear, visual way to see relationships between concepts. They help you organize your thoughts and can make abstract ideas more concrete. This visual representation aids in both comprehension and retention.
10. Chunking Information
Breaking down the text into manageable chunks can prevent you from feeling overwhelmed. Focus on one section at a time and take breaks if necessary. This technique is especially useful for dense or technical material.
Why it works: Chunking reduces cognitive load by allowing you to focus on smaller pieces of information at a time. It helps improve concentration and retention, as you can process and understand each part before moving on to the next.
11. Reading Aloud
Reading aloud can be a powerful strategy for improving comprehension. It forces you to slow down and pay attention to each word, which can be especially helpful for difficult or dense texts.
Why it works: Reading aloud engages multiple senses (seeing and hearing), which can enhance understanding and retention. It also helps you catch errors or misunderstandings that you might miss when reading silently.
12. Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing involves rephrasing the text in your own words. This can be done after reading a paragraph, section, or chapter.
Why it works: Paraphrasing ensures that you have understood the material. It also helps you internalize the information by actively processing it and expressing it in your own words.
13. Using Context Clues
When you encounter unfamiliar words or concepts, use the context around them to infer their meanings. Look at the sentences before and after the unfamiliar term for hints.
Why it works: Using context clues helps you understand the text without constantly stopping to look up words. It keeps the reading flow and enhances comprehension by using the surrounding information to make sense of unfamiliar terms.
14. Re-reading
Don’t hesitate to re-read challenging sections. Sometimes, going over the material a second or third time can provide clarity and deepen your understanding.
Why it works: Re-reading allows you to see details you might have missed the first time. It reinforces your memory and can help you understand complex ideas better.
15. Discussing the Text
Engage in discussions about what you’ve read with friends, family, or a reading group. Talking about the text can provide new insights and help reinforce your understanding.
Why it works: Discussion allows you to hear different perspectives and interpretations. It can clarify your understanding and help you remember the material by articulating your thoughts and hearing others’ viewpoints.
16. Practicing Regularly
Like any skill, reading comprehension improves with regular practice. Make reading a daily habit, and challenge yourself with diverse and increasingly complex materials.
Why it works: Consistent practice not only builds your comprehension skills but also keeps your mind sharp and adaptable to different types of texts and styles of writing.
17. Using Technology
There are numerous apps and online resources designed to improve reading comprehension. Tools like e-readers, which allow you to highlight text and take notes, or apps that provide comprehension questions and summaries, can be very helpful.
Why it works: Technology can provide additional support and resources that enhance your reading experience. It can offer interactive and engaging ways to improve comprehension.
18. Reading Actively
Active reading involves being fully engaged and involved with the text. This means not just passively reading the words but thinking critically about what you’re reading, asking questions, and making connections.
How to read actively:
- Highlight or underline key points.
- Write notes in the margins.
- Ask questions and seek answers as you read.
- Make predictions about what will happen next.
- Reflect on the text’s meaning and implications.
Why it works: Active reading keeps you engaged and makes the reading process more dynamic and interactive. It enhances understanding and retention by encouraging deeper involvement with the text.
19. Seeking Feedback
If you are reading for a class or group, seek feedback on your understanding. This can come from teachers, peers, or even online forums.
Why it works: Feedback helps you identify areas where you may need improvement. It provides different perspectives and can clarify misunderstandings, enhancing your overall comprehension.
20. Staying Healthy
Believe it or not, your physical health can impact your reading comprehension. Ensure you get enough sleep, maintain a balanced diet, and exercise regularly. A healthy body supports a healthy mind.
Why it works: Good physical health enhances cognitive function, including memory and concentration. It ensures that your brain is in the best condition to process and retain information.
Conclusion
Improving reading comprehension is a journey that involves engaging actively with the text, employing various strategies to deepen understanding, and reflecting on what you’ve learned. By previewing, setting a purpose, asking questions, visualizing, summarizing, making connections, reflecting, annotating, using graphic organizers, chunking information, reading aloud, paraphrasing, using context clues, re-reading, discussing, practicing regularly, using technology, reading actively, seeking feedback, and maintaining good health, you can enhance your ability to understand and retain information. Whether you’re reading for school, work, or pleasure, these strategies will help you get the
Best Comprehension Strategies