Why Phonics is a must in Early Literacy Development? -[Freebies Included]












Phonics is a method of teaching reading and writing by developing learners’ phonemic awareness—the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate phonemes—in order to teach the correspondence between these sounds and the spelling patterns (graphemes) that represent them. As one of the most effective approaches to literacy instruction, phonics is essential in early education. This article delves into the importance of phonics, exploring its role in literacy development, the benefits it offers, and best practices for implementing phonics instruction in the classroom.








Activity in phonics book
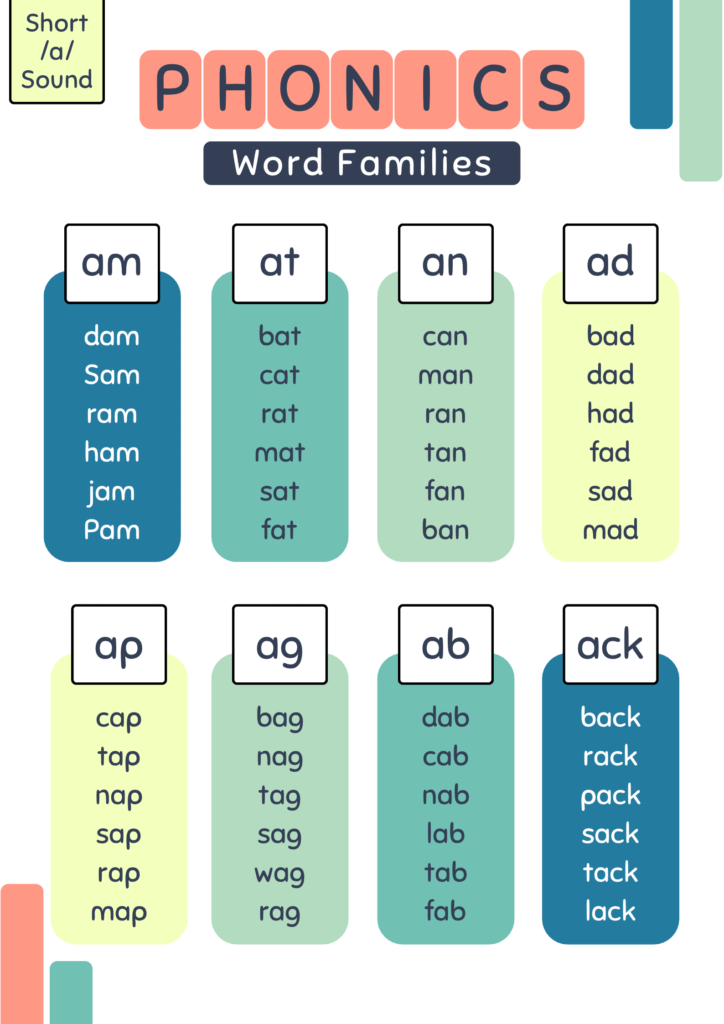
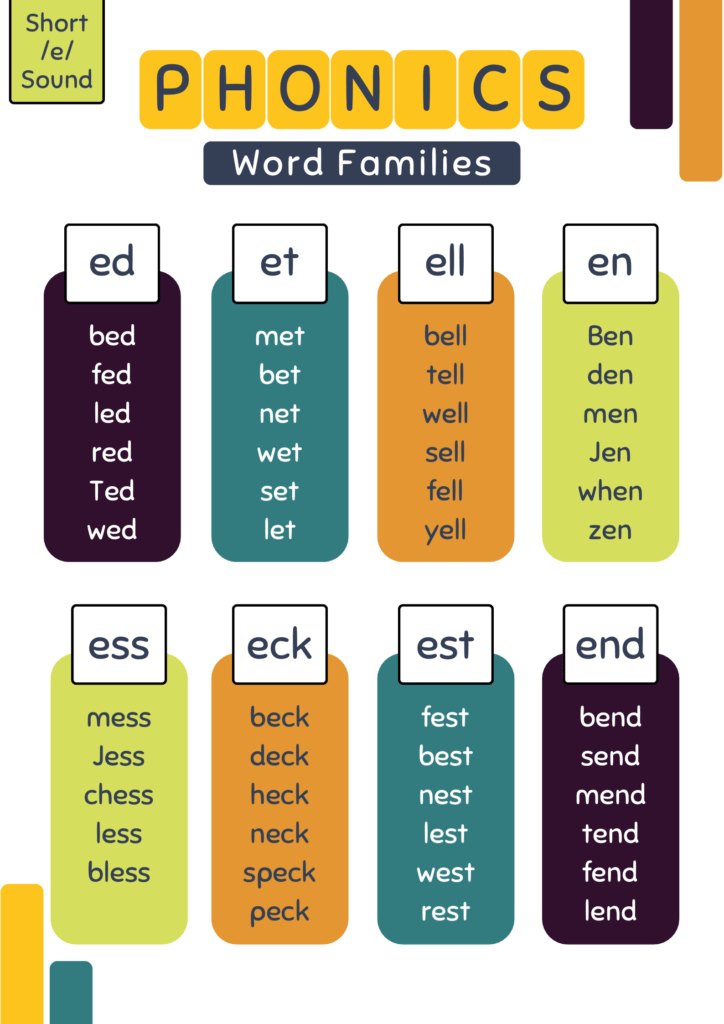
You May Also like: Comprehension for Kindergarten
You May Also like: Sight Words Worksheets

Download Phonics Workbook
Why Phonics is important?
You May Also like: Free Printables: Alphabet Worksheets
You may also like: Free Flashcards for kindergarten
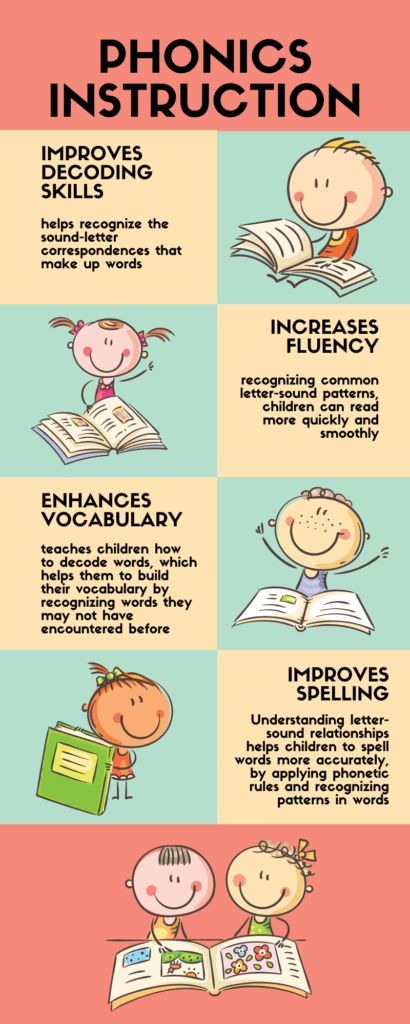
Understanding Phonics- Why Phonics is important
Phonics is grounded in the alphabetic principle, which is the understanding that letters and letter patterns represent the sounds of spoken language. This foundational knowledge is critical because it serves as the basis for word recognition, spelling, and reading comprehension. The core components of phonics instruction include:
- Phonemic Awareness: The ability to hear and manipulate the sounds in spoken words.
- Phoneme-Grapheme Correspondence: Understanding the relationship between sounds (phonemes) and their written symbols (graphemes).
- Decoding: The ability to blend sounds together to read words.
- Encoding: The ability to segment sounds to spell words.

Download Let’s Learn Phonics Workbook
The Role of Phonics in Literacy Development
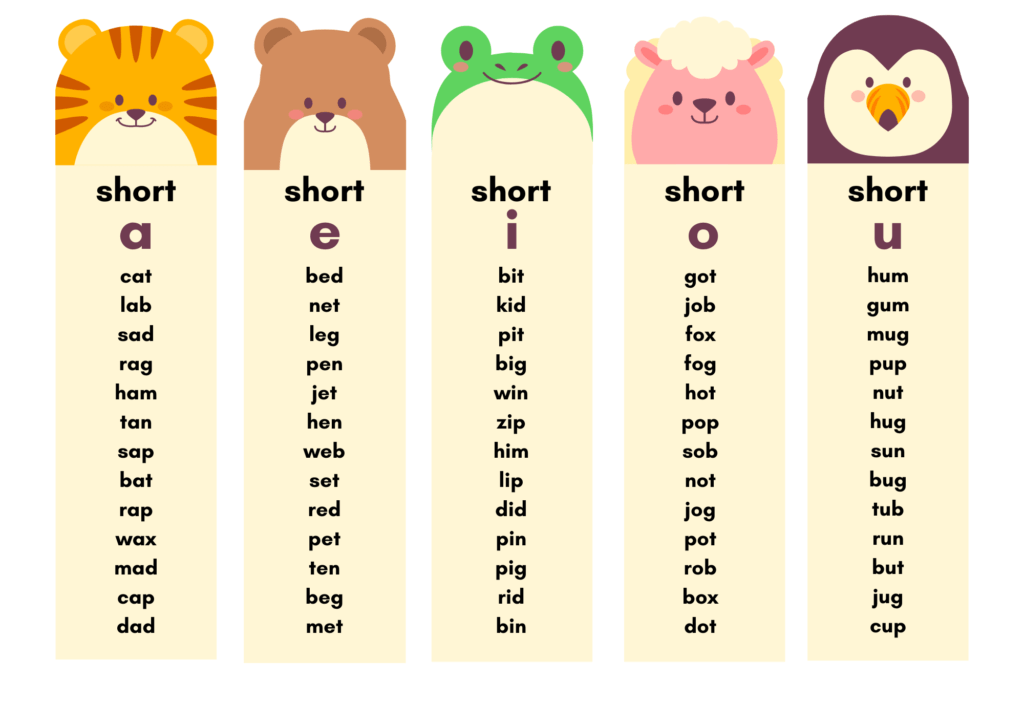

Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic awareness is the first step in the phonics learning process. Before children can understand the relationship between letters and sounds, they must first be able to hear and differentiate the sounds in words. Phonemic awareness activities might include rhyming, segmenting words into individual sounds, and blending sounds to form words. This skill is crucial because it lays the foundation for phonics instruction and helps children understand that words are made up of individual sounds that can be manipulated.
Download A Phonics game
Phoneme-Grapheme Correspondence
Once children are proficient in phonemic awareness, they can begin to learn phoneme-grapheme correspondence. This involves teaching children that specific letters or combinations of letters correspond to particular sounds. For example, children learn that the letter “b” represents the /b/ sound and that the combination “sh” represents the /ʃ/ sound. Mastery of these correspondences is essential for decoding (reading) and encoding (spelling) words.

Phonics Spelling Worksheet
Decoding and Word Recognition
Decoding is the process of translating written words into their spoken equivalents by sounding them out. Effective phonics instruction teaches children to apply their knowledge of phoneme-grapheme correspondences to decode unfamiliar words. As children become more proficient decoders, they begin to recognize words more quickly and accurately, which is crucial for fluent reading. Word recognition, a critical component of reading fluency, is heavily dependent on strong decoding skills developed through phonics instruction.
Spelling and Writing
Phonics instruction also plays a significant role in spelling and writing. By understanding the relationship between sounds and letters, children can more easily encode words when writing. Phonics helps children spell words correctly by applying rules and patterns they have learned, making their writing more accurate and comprehensible.
Benefits of Phonics Instruction

Download Magic E Worksheet- Why Phonics is important
Improved Reading Skills
Phonics instruction has been shown to improve reading skills significantly. Children who receive systematic, explicit phonics instruction are more likely to become proficient readers. They develop the ability to decode words accurately and fluently, which leads to better reading comprehension. Research consistently shows that early phonics instruction improves children’s ability to read and spell words, leading to greater success in reading overall.
Enhanced Comprehension
Fluent reading is closely linked to comprehension. When children can decode words effortlessly, they can focus more on understanding the meaning of the text rather than struggling to identify individual words. Phonics instruction provides the skills necessary for automatic word recognition, freeing cognitive resources for comprehension. Consequently, children who receive effective phonics instruction are better able to understand and engage with the texts they read.
Greater Confidence and Motivation
Children who struggle with reading often experience frustration and a lack of confidence. Phonics instruction helps to build a strong foundation in reading, enabling children to approach reading tasks with greater confidence. As their decoding and word recognition skills improve, so does their motivation to read. This increased confidence and motivation can lead to a more positive attitude towards reading and learning in general.
Support for English Language Learners
Phonics instruction is particularly beneficial for English Language Learners (ELLs). Learning the sound-letter relationships of English can be challenging for ELLs, especially if their first language has a different phonetic system. Systematic phonics instruction provides ELLs with a structured approach to understanding how English works, helping them to decode words and improve their reading and writing skills in their new language.
Best Practices for Phonics Instruction
Systematic and Explicit Instruction
Phonics instruction should be systematic and explicit. This means that phonics skills should be taught in a planned, sequential order, starting with the simplest and most common sound-letter relationships and progressing to more complex ones. Explicit instruction involves directly teaching these relationships and providing clear, concise explanations and demonstrations. This approach ensures that children understand the connections between letters and sounds and can apply this knowledge to reading and writing.
Integration with Other Literacy Skills
While phonics is a critical component of early literacy instruction, it should not be taught in isolation. Effective phonics instruction is integrated with other literacy skills, including vocabulary development, reading comprehension, and writing. By incorporating phonics into a broader literacy curriculum, teachers can help children develop a more comprehensive understanding of language and its use.
Use of Multisensory Techniques
Multisensory techniques, which engage multiple senses, can enhance phonics instruction. Activities that involve seeing, hearing, speaking, and touching can help reinforce phonics concepts. For example, children might trace letters in sand while saying the corresponding sound or use magnetic letters to build words. These multisensory approaches can make phonics instruction more engaging and effective.
Differentiation to Meet Individual Needs
Children come to the classroom with varying levels of phonemic awareness and phonics knowledge. Effective phonics instruction requires differentiation to meet the diverse needs of learners. Teachers can use assessments to identify each child’s strengths and weaknesses and tailor instruction accordingly. Small group instruction, targeted interventions, and individualized activities can help ensure that all children receive the support they need to succeed.
Ongoing Assessment and Progress Monitoring
Regular assessment and progress monitoring are essential components of effective phonics instruction. Teachers should use formative assessments to track students’ progress and identify areas where additional support is needed. This ongoing assessment helps to ensure that children are making steady progress in their phonics skills and allows teachers to adjust instruction as necessary to address any gaps in learning.
Challenges and Considerations
Balancing Phonics with Other Approaches
While phonics is a highly effective approach to literacy instruction, it is important to balance it with other methods. The “whole language” approach, which emphasizes reading for meaning and using context to identify words, can complement phonics instruction. By integrating phonics with whole language strategies, teachers can provide a more holistic approach to reading instruction that addresses both decoding and comprehension skills.
Addressing Diverse Learning Styles
Children have different learning styles and preferences. Some may respond well to visual and auditory instruction, while others may benefit more from hands-on, kinesthetic activities. Effective phonics instruction should incorporate a variety of teaching methods and materials to cater to diverse learning styles. This approach can help ensure that all children are engaged and able to learn in a way that suits them best.
Ensuring Equity in Instruction
Equity in phonics instruction is crucial to ensure that all children have the opportunity to succeed in reading. This means providing high-quality phonics instruction to all students, regardless of their background or prior knowledge. Teachers should be aware of and address any potential barriers to learning, such as language differences, learning disabilities, or socio-economic factors, to create an inclusive and supportive learning environment.
Conclusion – Why Phonics is important
Phonics is a fundamental component of early literacy instruction, providing children with the essential skills needed to decode words, spell accurately, and comprehend texts. The benefits of phonics instruction are well-documented, with research showing its effectiveness in improving reading skills, enhancing comprehension, and boosting confidence and motivation. By implementing systematic, explicit phonics instruction and integrating it with other literacy skills, teachers can help children develop a strong foundation in reading and writing. Addressing the diverse needs of learners through differentiated instruction, multisensory techniques, and ongoing assessment ensures that all children have the opportunity to become proficient readers. As educators, recognizing the importance of phonics and employing best practices in instruction is key to fostering literacy development and setting students on the path to academic success.